Main Article Content
Abstract
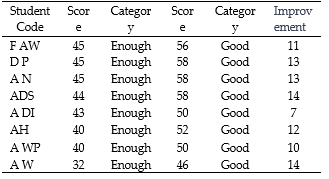
Critical thinking skills are a crucial aspect of education aimed at equipping students with strong analytical abilities, deep understanding, and effective problem-solving skills. The primary objective of this study is to assess the impact of implementing the talking-stick-playing strategy during group guidance sessions on the enhancement of critical thinking skills among students majoring in Guidance and Counseling at Bengkulu University. The research methodology employed in this investigation is experimental, utilizing a one-group pretest-posttest design. Participant selection involved purposive sampling, with a sample size of eight students from 29 students. Data collection used the critical thinking ability scale adapted from Purnomo (2020), comprising 5 dimensions and 15 statement items. Analytical techniques were using descriptive analysis and Wilcoxon test analysis. Findings from the descriptive analysis reveal that students' critical thinking abilities were categorized as sufficient before the intervention, but improved to a good level after the treatment. Furthermore, the Wilcoxon test results yielded an Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) value of 0.000, indicating that the implementation of the talking-stick strategy during group guidance sessions significantly influences the development of students' critical thinking skills. This indicates that the structured and participatory communication method introduced through the Talking-Stick helps students develop their critical thinking skills. Therefore, this approach should be considered by educators and counsellors as a valuable resource in enriching students' learning experiences in higher education.
Keywords
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
References
- Akhir, M. (2018). Integrasi Pendidikan Karakter Dalam Meningkatkan Keterampilan Menulis Mahasiswa Di Perguruan Tinggi. Prosiding Seminar Nasional Pendidikan, 1(1).
- Aly, A. (2017). Pengembangan pembelajaran karakter berbasis soft skills di perguruan tinggi. Ishraqi, 1(1), 18–30. https://doi.org/10.23917/ishraqi.v1i1.2926
- Anggraini, A. N., & Fitrawati, F. (2016). Teaching Speaking By Using Talking Stick Technique for Senior High School Students. Journal of English Language Teaching, 5(1), 72–79. https://doi.org/10.24036/jelt.v5i1.7272
- Anidar, J., Neviyarni, N., Nirwana, H., & Khairani, K. (2023, August). Classical guidance and counseling model with open-ended techniques to improve ability critical thinking learners: The study of the practicality of the model. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 2805, No. 1). AIP Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0149907
- Aziza, M. (2021). A teacher questioning activity: The use of oral open-ended questions in mathematics classroom. Qualitative Research in Education, 10(1), 31-61. https://doi.org/10.17583/qre.2021.6475
- Bucklin, B. A., Asdigian, N. L., Hawkins, J. L., & Klein, U. (2021). Making it stick: use of active learning strategies in continuing medical education. BMC medical education, 21, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-020-02447-0
- Cefai, C., Bartolo, P. A., Cavioni, V., & Downes, P. (2018). Strengthening social and emotional education as a core curricular area across the EU: A review of the international evidence.
- Chen, D. L. (2015). Developing critical thinking through problem-based learning: an action research for a class of media literacy [Doctoral dissertation, Durham University].
- Chen, M., & Rybak, C. (2017). Group leadership skills: Interpersonal process in group counseling and therapy. Sage Publications.
- Chen, H., Tang, Y., & Han, J. (2022). Building students’ entrepreneurial competencies in chinese universities: Diverse learning environment, knowledge transfer, and entrepreneurship education. Sustainability, 14(15), 9105. https://doi.org/10.3390/su14159105
- Chin, C. (2007). Teacher questioning in science classrooms: Approaches that stimulate productive thinking. Journal of Research in Science Teaching: The Official Journal of the National Association for Research in Science Teaching, 44(6), 815-843. https://doi.org/10.1002/tea.20171
- Corbisiero, F., Monaco, S., & Ruspini, E. (2022). Millennials, Generation Z and the future of tourism (Vol. 7). Channel View Publications.
- Cottrell, S. (2017). Critical thinking skills: Effective analysis, argument and reflection (Vol. 100). Bloomsbury Publishing.
- Eldeleklioğlu, J., & ÖZKILIÇ, R. (2008). The effect of critical thinking education on critical thinking skills of psychological guidance and counseling students. Turkish Psychological Counseling and Guidance Journal, 3(29), 25–36. https://doi.org/10.17066/pdrd.66129
- Ferrari, A., Cachia, R., & Punie, Y. (2009). Innovation and creativity in education and training in the EU member states: Fostering creative learning and supporting innovative teaching. JRC Technical Note, 52374, 64.
- Finlay, L. (2011). Phenomenology for therapists: Researching the lived world. John Wiley & Sons.
- Gafur, H. (2015). Mahasiswa & Dinamika Dunia Kampus. Rasibook.
- Greenstein, L. M. (2012). Assessing 21st century skills: A guide to evaluating mastery and authentic learning. Corwin Press.
- Hawkins, D., Elder, L., & Paul, R. (2019). The Thinker’s Guide to Clinical Reasoning: Based on Critical Thinking Concepts and Tools. Rowman & Littlefield.
- Heard, J., Scoular, C., Duckworth, D., Ramalingam, D., & Teo, I. (2020). Critical thinking: Skill development framework.
- Høffding, S., & Martiny, K. (2016). Framing a phenomenological interview: what, why and how. Phenomenology and the Cognitive Sciences, 15, 539–564. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11097-015-9433-z
- Hsu, F.-H., Lin, I.-H., Yeh, H.-C., & Chen, N.-S. (2022). Effect of Socratic Reflection Prompts via video-based learning system on elementary school students’ critical thinking skills. Computers & Education, 183, 104497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104497
- Huang, H. M., Rauch, U., & Liaw, S. S. (2010). Investigating learners’ attitudes toward virtual reality learning environments: Based on a constructivist approach. Computers & Education, 55(3), 1171-1182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2010.05.014
- Irwin, H. (2020). Communicating with Asia: Understanding people and customs. Routledge.
- Jannah, A. U., & Wirastania, A. (2022). Bimbingan kelompok dengan teknik permainan talking stick dalam meningkatkan kemampuan berpendapat siswa. TERAPUTIK: Jurnal Bimbingan dan Konseling, 6(1), 1-7. https://doi.org/10.26539/teraputik.61960
- Jääskä, E., & Aaltonen, K. (2022). Teachers’ experiences of using game-based learning methods in project management higher education. Project Leadership and Society, 3, 100041.
- Kelly, R., O’Malley, M. P., & Antonijevic, S. (2018). ‘Just trying to talk to people… It’s the hardest’: Perspectives of adolescents with high-functioning autism spectrum disorder on their social communication skills. Child language teaching and therapy, 34(3), 319-334. https://doi.org/10.1177/0265659018806754
- Kuhn, D. (2019). Critical thinking as discourse. Human Development, 62(3), 146–164. https://doi.org/10.1159/000500171
- Lai, E. R. (2011). Critical thinking: A literature review. Pearson’s Research Reports, 6(1), 40–41.
- Larsson, K. (2017). Understanding and teaching critical thinking—A new approach. International Journal of Educational Research, 84, 32–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2017.05.004
- Lazonder, A. W., & Harmsen, R. (2016). Meta-analysis of inquiry-based learning: Effects of guidance. Review of Educational Research, 86(3), 681–718. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654315627366
- Lester, M. (2011). A study of the innovation, creativity, and leadership skills associated with the college-level millennial generation. Pepperdine University.
- Lewis, A., & Smith, D. (1993). Defining higher order thinking. Theory into Practice, 32(3), 131–137.
- Liang, W., & Fung, D. (2021). Fostering critical thinking in English-as-a-second-language classrooms: Challenges and opportunities. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 39, 100769
- Liedtka, J. (2015). Perspective: Linking design thinking with innovation outcomes through cognitive bias reduction. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 32(6), 925–938. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12163
- Maksum, A., Widiana, I. W., & Marini, A. (2021). Path Analysis of Self-Regulation, Social Skills, Critical Thinking and Problem-Solving Ability on Social Studies Learning Outcomes. International Journal of Instruction, 14(3), 613–628.
- Marcus, G. (2018). Deep learning: A critical appraisal. ArXiv Preprint ArXiv:1801.00631.
- Marisa, R. (2022). The Application of Talking Stick Method In Improving Students’ Speaking Ability [Doctoral dissertation, UIN Ar-Raniry].
- Morard, S., Sanchez, E., & Bonnat, C. (2023). Museum Games and Personal Epistemology: A Study on Students’ Critical Thinking with a Mixed Reality Game. International Journal of Serious Games, 10(4), 131-151. https://doi.org/10.17083/ijsg.v10i4.695
- Müller, R., & de Rijcke, S. (2017). Thinking with indicators. Exploring the epistemic impacts of academic performance indicators in the life sciences. Research Evaluation, 26(3), 157–168. https://doi.org/10.1093/reseval/rvx023
- Munawarah, M., & Abshari, R. (2019). Pengembangan Soft Skills Dan Relevansinya Terhadap Pembentukan Akhlak Mahasiswa: Perspektif Hadis. Jurnal Ilmiah Mahasiswa Raushan Fikr, 8(1), 83–97. https://doi.org/10.24090/jimrf.v8i1.3056
- Mustari, M. (2022). Manajemen pendidikan di era merdeka belajar. Prodi S2 Studi Agama-Agama UIN Sunan Gunung Djati Bandung.
- Nadeak, B., & Naibaho, L. (2020). The effectiveness of problem-based learning on students’critical thinking. Jurnal Dinamika Pendidikan, 13(1), 1–7. https://doi.org/10.51212/jdp.v13i1.1393
- Nida, D. M. A. A., Parmiti, D. P., & Sukmana, A. I. W. I. Y. (2020). Pengembangan media kartu bergambar berorientasi pendidikan karakter pada mata pelajaran bahasa bali. Jurnal Edutech Undiksha, 8(1), 16–31. https://doi.org/10.23887/jeu.v8i1.25393
- Nobutoshi, M. (2023). Metacognition and Reflective Teaching: A Synergistic Approach to Fostering Critical Thinking Skills. Research and Advances in Education, 2(9), 1-14.
- Nursing, A. A. of C. of. (2009). American Association of Colleges of Nursing-AACN.
- Pithers, R. T., & Soden, R. (2000). Critical thinking in education: A review. Educational research, 42(3), 237-249. https://doi.org/10.1080/001318800440579
- Pohan, R. A. (2016). Kontribusi kepercayaan diri dan persepsi siswa terhadap kegiatan merespon dalam pembelajaran serta implikasinya dalam bimbingan dan konseling. Jurnal Penelitian Bimbingan dan Konseling, 1(2). http://dx.doi.org/10.30870/jpbk.v1i2.1872
- Pohan, R. A., & Indra, S. (2020). Efektivitas layanan bimbingan kelompok dalam meningkatkan kegiatan merespon pembelajaran. Islamic Counseling: Jurnal Bimbingan Konseling Islam, 4(1), 17-30. http://dx.doi.org/10.29240/jbk.v4i1.1280
- Prajapati, R., Sharma, B., & Sharma, D. (2017). Significance of life skills education. Contemporary Issues in Education Research (CIER), 10(1), 1–6. https://doi.org/10.19030/cier.v10i1.9875
- Pratiwi, I. (2022). Penerapan Model Problem Based Learning Berbantuan Audio Visual Untuk Meningkatkan Kemampuan Berpikir Kritis dan Hasil Belajar Siswa. Journal of Education Action Research, 6(3). https://doi.org/10.23887/jear.v6i3.49668
- Purnomo, R. W. (2020). Pengaruh Kreativitas Guru Terhadap Berpikir Kritis Peserta Didik SMP Sekecamatan Gresik. Universitas Muhamadiyah Gresik.
- Putri, L. C. (2019). Efeektivitas Model Pembelajaran Talking Stick Terhadap Kemampuan Berpikir Kritis Peserta Didik (Doctoral dissertation, UIN Raden Intan Lampung).
- Renatovna, A. G., & Renatovna, A. S. (2021). Pedagogical and psychological conditions of preparing students for social relations on the basis of the development of critical thinking. Psychology and Education Journal, 58(2), 4889–4902.
- Restian, A., Muzakki, A., & Purnamasari, W. I. (2020). Model pembelajaran talking stick melalui permainan truth or dare pada tari bungong jeumpa kelas IV sekolah dasar. Jurnal Satwika, 4(1), 1–9. https://doi.org/10.22219/satwika.v4i1.11435
- Saihu, S. (2020). The Effect of Using Talking Stick Learning Model on Student Learning Outcomes in Islamic Primary School of Jamiatul Khair, Ciledug Tangerang. Tarbawi: Jurnal Keilmuan Manajemen Pendidikan, 6(01), 61-68. https://doi.org/10.32678/tarbawi.v6i01.2325
- Salazar, A. M., Jones, K. R., Emerson, J. C., & Mucha, L. (2016). Postsecondary strengths, challenges, and supports experienced by foster care alumni college graduates. Journal of College Student Development, 57(3), 263–279. https://doi.org/10.1353/csd.2016.0029
- Schooner, P., Nordlöf, C., Klasander, C., & Hallström, J. (2017). Design, System, Value: The Role of Problem-Solving and Critical Thinking Capabilities in Technology Education, as Perceived by Teachers. Design and Technology Education, 22(3), n3.
- Scouten, R. W., Wesson, M., Wetherill, L., Vance, G. H., & Delk, P. R. (2023). Genetic counseling program remediation practices for students underperforming in clinical skills: An exploratory study. Journal of Genetic Counseling. https://doi.org/10.1002/jgc4.1710
- Shah, M., & Pabel, A. (2020). Making the student voice count: Using qualitative student feedback to enhance the student experience. Journal of Applied Research in Higher Education, 12(2), 194–209. https://doi.org/10.1108/JARHE-02-2019-0030
- Shechtman, Z. (2017). Group counseling and psychotherapy with children and adolescents: Theory, research, and practice. Routledge.
- Siahaan, R., Sitorus, M., & Silaban, S. (2021). The development of teaching materials oriented to critical thinking skills for chemistry class XI high school. Jurnal Pendidikan Kimia, 13(1), 60–68. https://doi.org/10.24114/jpkim.v13i1.24145
- Sternberg, R. J. (1986). Critical Thinking: Its Nature, Measurement, and Improvement.
- Suryaningsih, A., & Koeswanti, H. D. (2021). Perbedaan Model Pembelajaran Problem Based Learning dan Project Based Learning Terhadap Peningkatan Kemampuan Berfikir Kritis IPA Siswa SD. MIMBAR PGSD Undiksha, 9(1), 40–48. https://doi.org/10.23887/jjpgsd.v9i1.33196
- Suter, W. N. (2011). Introduction to educational research: A critical thinking approach. SAGE publications.
- Springer, C., & Misurell, J. R. (2010). Game-based cognitive-behavioral therapy (GB-CBT): An innovative group treatment program for children who have been sexually abused. Journal of Child & Adolescent Trauma, 3, 163-180. https://doi.org/10.1080/19361521.2010.491506
- Tangahu, O. (2023). Increase Participant Activities And Learning Outcomes Educate Through The Talking Stick Learning Model In Science Subjects In Class Viii Smp Negeri 8 Gorontalo. Open Access Repository, 9(4), 58-73. https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/92JZ8
- Treffinger, D. J., Isaksen, S. G., & Stead-Dorval, K. B. (2023). Creative problem solving: An introduction. Routledge.
- Turan, U., Fidan, Y., & Yıldıran, C. (2019). Critical thinking as a qualified decision making tool. Journal of History Culture and Art Research, 8(4), 1–18. https://doi.org/10.7596/taksad.v8i4.2316
- Tyas, E. H., & Naibaho, L. (2021). HOTS learning model improves the quality of education. International Journal of Research-GRANTHAALAYAH, 9(1), 176–182.
- Ulger, K. (2018). The effect of problem-based learning on the creative thinking and critical thinking disposition of students in visual arts education. Interdisciplinary Journal of Problem-Based Learning, 12(1). https://doi.org/10.7771/1541-5015.1649
- Wagner, T. (2008). The Global Achievement Gap: Why Our Kids Don't Have the Skills They Need for College, Careers, and Citizenship—and What We Can Do About It. Basic Books.
- Wicaksono, H. T., & Koeswanti, H. D. (2019). Penerapan Model Pembelajaran Talking Stick Berbasis Scientific Untuk Meningkatkan Hasil Belajar Muatan Matematika. Holistika: Jurnal Ilmiah PGSD, 3(1), 29–36. https://doi.org/10.24853/holistika.3.1.29-36
- Widana, I. W., Parwata, I., & Sukendra, I. K. (2018). Higher order thinking skills assessment towards critical thinking on mathematics lesson. International Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities, 2(1), 24–32.
- Winter, J. (2016). Thinking about Silence 1. In Aftermath (pp. 183–198). Routledge.
- Wulandari, V., & SETIAWATI, D. (2019). Penerapan Layanan Konseling Kelompok Dengan Teknik Modeling Partisipan Untuk Meningkatkan Percaya Diri Siswa Saat Mengemukakan Pendapat Pada Kelas XI IPS 3 DI SMAN 2 Karangan. Bk Unesa, 9(2), 14–27.
- Zare, P., & Othman, M. (2015). Students’ perceptions toward using classroom debate to develop critical thinking and oral communication ability. Asian Social Science, 11(9), 158. https://doi.org/10.5539/ass.v11n9p158